Table of Contents
In this article, we discuss the AMD Gorgon Point hardware platform, launched in early 2026, which powers the majority of AMD laptops available this year and into the first part of 2027.
Gorgon Point is a mid-cycle refresh of the existing AMD Strix Point and AMD Krackan Point platforms discussed in previous articles. That means the Ryzen AI 400 Series APUs are built on the same core technology as past AMD hardware, featuring a mix of Zen5 performance and Zen5c efficiency processor cores, along with Radeon iGPUs that utilize RDNA3.5 Compute Cores. Compared to the Ryzen AI 300 predecessors, Gorgon Point offers minor refinements and updates in clock speeds – however, some of the devices built on this hardware do offer updated designs and features for this year.
Much like in the past, the upper-tier processors are the Ryzen AI 9 SKUs, while the mid and lower-tier options are the Ryzen AI 7 and AI 5 options. The two implement the same CPU/GPU technology, just with fewer cores and lower speeds as we go down the lineup.
However, it’s important to understand that Gorgon Point is not a major hardware refresh. That’s only coming in 2027 with the AMD Medusa Halo and Halo Mini platforms (naming still to be confirmed), with Zen6/Zen6c CPU cores (up to 26C/52T), updated graphics built on RDNA5 cores (up to 48 CUs), and support for LPDDR6 memory. But these are at least a year out at the time I’m writing this article, so Gorgon Point is all we’re getting this year for portable laptops, alongside Strix Halo for select higher-performance options and Fire Range HX for a handful of full-size high-performance notebooks.
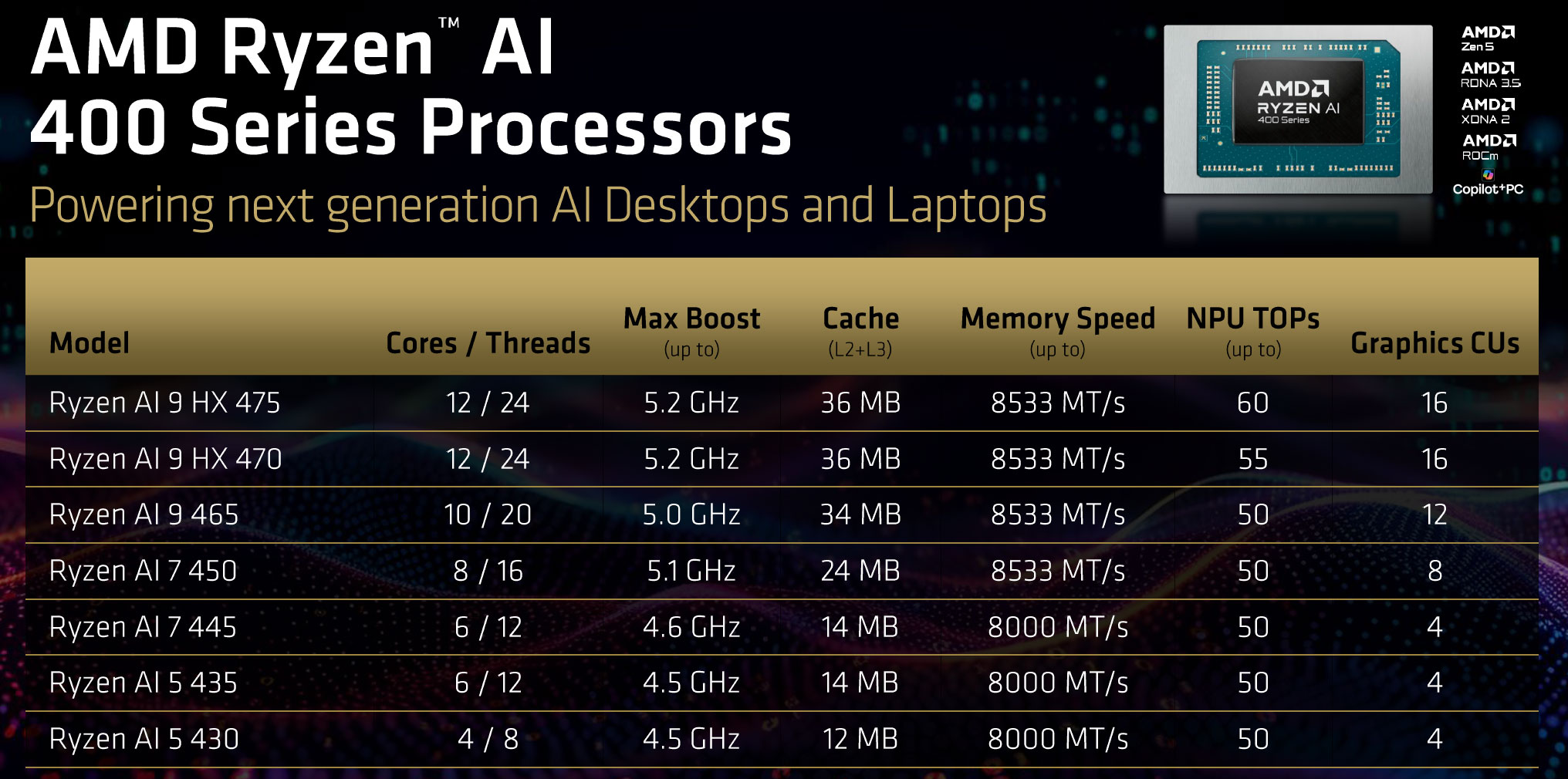
So let’s dive into these Ryzen AI 400 lineups and figure out what they’re all about. Here’s preview of the entire CPU roster.
While AMD no longer offers these as separate sub-lineups as with the Ryzen AI 300 generations, we should still discuss the Ryzen AI 9 and Ryzen AI 7/5 options separately, since they are meant for different kinds of devices.
So here are the three Gorgon Point Ryzen AI 9 400 SKUs (Ryzen AI 9 HX 475, Ryzen AI 9 HX 470, and Ryzen AI 9 465), next to their Strix Point Ryzen AI 300 counterparts that they are replacing.
You’ll mostly find these in more powerful notebooks between 14 and 16 inches in size, sometimes paired with Nvidia dedicated GPUs, especially in the larger models.
| Ryzen AI 9 HX 475 / HX 470 |
Ryzen AI 9 465 |
Ryzen AI 9 HX 375 / HX 370 |
Ryzen AI 9 365 |
|
| Build process | TSMC 4nm FinFET | |||
| Generation | Gorgon Point Zen5, Zen5c |
Strix Point Zen5, Zen5c |
||
| TDP | 15-54 W | |||
| Cores/Threads | 4x Zen5, 8x Zen5c, 24 Threads |
4x Zen5, 6x Zen5c, 20 Threads |
4x Zen5, 8x Zen5c, 24 Threads |
4x Zen5, 6x Zen5c, 20 Threads |
| CPU Max Turbo | up to 5.2 GHz – Zen5, up to 3.3 GHz – Zen5c |
up to 5.0 GHz – Zen5, up to 3.3 GHz – Zen5c |
up to 5.1 GHz – Zen5, up to 3.3 GHz – Zen5c |
up to 5.0 GHz – Zen5, up to 3.3 GHz – Zen5c |
| L2+L3 Cache | 36 MB | 34 MB | 36 MB | 34 MB |
| Memory Type | DDR5-5600, LPDDR5x-8533 | DDR5-5600, LPDDR5x-8000 | ||
| Graphics | Radeon 890M, 16x RDNA3.5 CUs, up to 3.1 GHz |
Radeon 880M, 12x RDNA3.5 CUs, up to 2.9 GHz |
Radeon 890M, 16x RDNA3.5 CUs, up to 2.9 GHz |
Radeon 880M, 12x RDNA3.5 CUs, up to 2.9 GHz |
| AI Engine | NPU – up to 60 TOPS (R 475) Total – up to 91 TOPS (R 475) NPU – up to 55 TOPS (R 470) Total – up to 86 TOPS (R 470) |
NPU – up to 50 TOPS Total – up to 73 TOPS |
NPU – up to 55 TOPS (R 375) Total – up to 85 TOPS (R 375) NPU – up to 50 TOPS (R 370) Total – up to 80 TOPS (R 370) |
NPU – up to 50 TOPS Total – up to 73 TOPS |
Very little to nothing has changed:
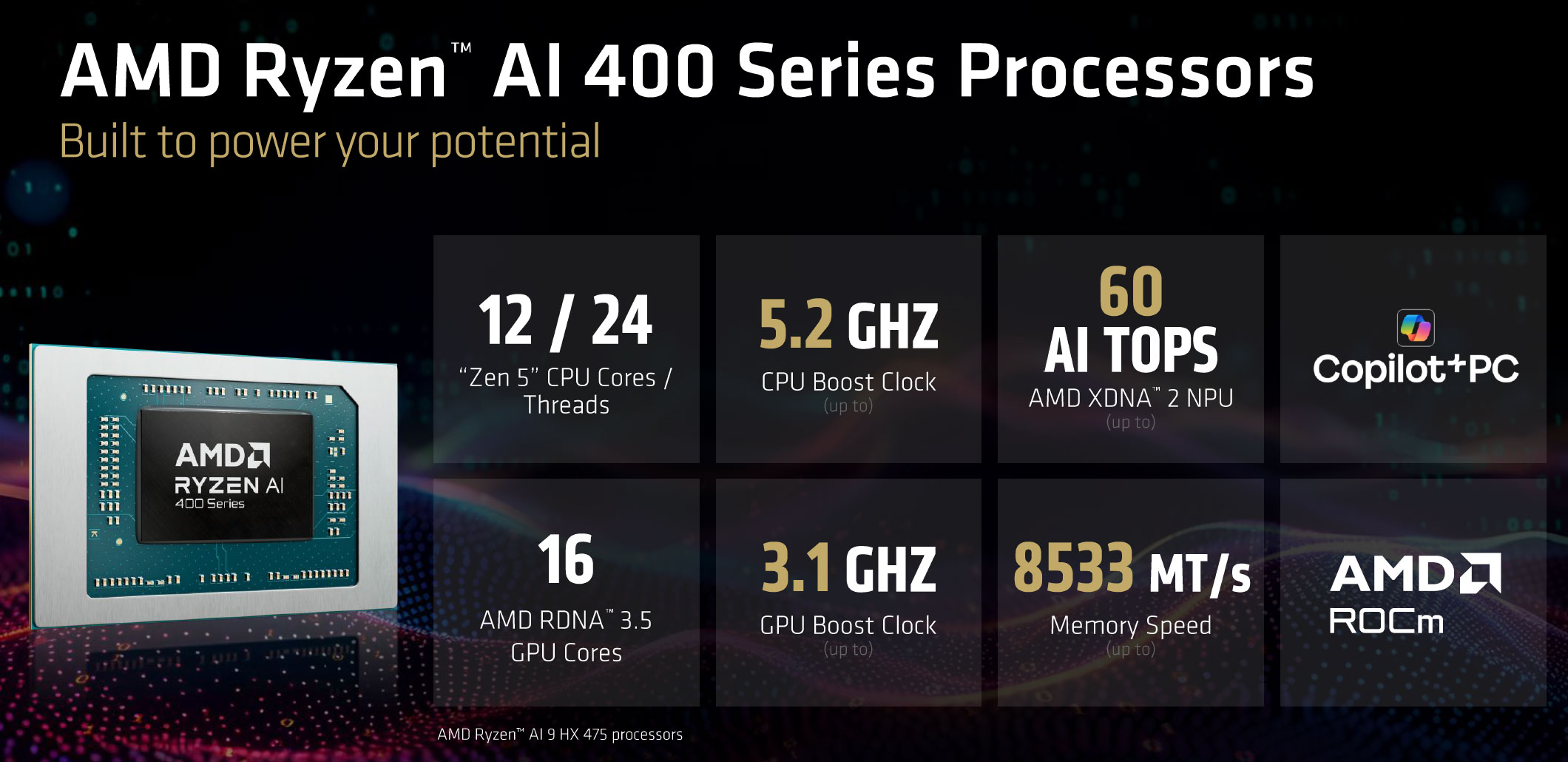
- a minor bump in CPU and GPU maximum Turbo speeds – but keep in mind that the iGPU only runs at full speeds in the more powerful designs at 40+W sustained;
- support for faster LPDDR5x-8533 memory (still 128-bit memory bus);
- an updated NPU that allows 60 TOPS on the Ryzen AI 9 HX 475 (still an XDNA 2 architecture);
The Ryzen AI 9 HX 475 and HX 470 are still identical with 12C/24T and a Radeon 890M iGPU with 16 Compute Units, with just the updated NPU on the 475; expect most retail notebooks to be built around the 470 SKU.
The Ryzen AI 9 465 slots in beneath the AI 9 HX options, with 10C/20T (but still 4x Zen5 main cores) and a Radeon 880M with 12 Compute Units. It’s still competitive on the CPU side, at 5-10% slower than the 470/475 options in sustained loads, something to keep in mind if you’re after a device that pairs the AMD processor with a dGPU. In fact, more OEMs choose to implement the Ryzen AI 9 465 on their 2026 models than before. At the same time, it’s not as competitive on the iGPU side, with 25% fewer graphics cores – something to keep in mind when looking at a device that relies entirely on the iGPU and lacks a dGPU.
All these being said, there’s no wonder some OEMs chose not to update their devices to Gorgon Point and keep offering their Strix Point implementations for 2026.
When it comes to these higher-tier Ryzen AI 9 SKUs, this platform is just a name update. So, if you’re choosing a 2026 model over a 2025 variant, make sure you’re doing it for other reasons and not for any performance/efficiency benefits that you would expect from the Ryzen AI 9 400 series hardware. However, we can hope for better availability and more affordable pricing with this hardware generation, all things considered.
Of course, there are still differences to account for between implementations, with regards to the power settings and cooling capacity of each device. When it comes to the more portable options, expect those to run at 25-35W sustained, while the larger formats can allow up to 80W of sustained power, even if in theory the hardware is only a 15-54W design – that just means it already runs at almost its best at 54W and a higher-power allocation doesn’t change performance in a significant way. You’ll have to look into specific details for more information on the performance and capabilities of each unit.
With these out of the way, here are the Gorgon Point Ryzen AI 7/5 400 SKUs next to their Krackan Point Ryzen AI 300 counterparts that they are replacing. You’ll mostly find these in mid-range portable models between 14 and 16 inches in size, generally as standalone implementations. There are a couple of other lower-tier Ryzen 5 and Ryzen 3 SKUs with 4C/8T and 4 CUs iGPU that I haven’t included here, targeted at budget-tier devices.
| Ryzen AI 7 450 |
Ryzen AI 7 445, Ryzen AI 5 435 |
Ryzen AI 7 350 | Ryzen AI 5 340 | |
| Build process | TSMC 4nm FinFET | |||
| Generation | Gorgon Point Zen5, Zen5c |
Krackan Point Zen5, Zen5c |
||
| TDP | 15-54 W | |||
| Cores/Threads | 4x Zen5, 4x Zen5c, 16 Threads |
2x Zen5, 4x Zen5c, 12 Threads |
4x Zen5, 4x Zen5c, 16 Threads |
3x Zen5, 3x Zen5c, 12 Threads |
| CPU Max Turbo | up to 5.1 GHz – Zen5, up to 3.6 GHz – Zen5c |
up to 4.6 GHz – Zen5, up to 3.4 GHz – Zen5c |
up to 5.0 GHz – Zen5, up to 3.5 GHz – Zen5c |
up to 4.8 GHz – Zen5, up to 3.4 GHz – Zen5c |
| L2+L3 Cache | 24 MB | 14 MB | 24 MB | 22 MB |
| Memory Type | DDR5-5600, LPDDR5x-8000 | |||
| Graphics | Radeon 860M, 8x RDNA3.5 CUs, up to 3.1 GHz |
Radeon 840M, 4x RDNA3.5 CUs, up to 2.9 GHz – R 445 up to 2.8 GHz – R 435 |
Radeon 860M, 8x RDNA3.5 CUs, up to 2.9 GHz |
Radeon 840M, 4x RDNA3.5 CUs, up to 2.9 GHz |
| AI Engine | NPU – up to 50 TOPS Total – up to 66 TOPS |
NPU – up to 50 TOPS Total – up to 59 TOPS |
NPU – up to 50 TOPS Total – up to 66 TOPS |
NPU – up to 50 TOPS Total – up to 59 TOPS |
The Ryzen AI 7 450 remains a competitive mid-tier processor with still 8Cores and 8x CUs on the iGPU. That’s plenty capable for a lightweight and compact device, and based on our experience with the Ryzen AI 7 350 models we’ve tested, the hardware is going to run efficiently and quietly as well.
At the same time, the changes are once more minor to none over the Ryzen AI 7 350 that it replaces, with still minimal increases in CPU/GPU clock speeds.
The lower-tier Ryzen AI 7/5 models are different from those in the past, though, as they implement a 2x Zen5, 4x Zen5c configuration on the CPU side, alongside a Radeon 840M iGPU with only 4x CUs. In the past, the Ryzen AI 5 340 implemented 3x Zen5 with 3x Zen5c cores in a somewhat more capable CPU.
Furthermore, the addition of the Ryzen AI 7 445 SKU will confuse buyers, as this is identical in features and specs to the Ryzen AI 5 435, with minimal increases in CPU/GPU max clocks. And that means potential buyers could choose a Ryzen AI 7 445 notebook hoping it’s a better processor than the Ryzen AI 5 435, even if in reality it is not. I would have preferred a leaner lineup of Ryzen AI 7 and AI 5 options.
On top of that, many notebook lineups that previously shipped with a Ryzen AI 7 350 now top at a Ryzen AI 7 445 (Asus Zenbook 14, Lenovo Yoga 7a 2-in-1, to name just some of the more popular ones). For general use, that’s still a fine processor, but not as competent for sustained loads. I just hope the explanation is a cheaper price and improved availability compared to the the 8C Ryzen AI 7 versions.
Ryzen AI 9 HX 470 / 465 and Ryzen AI 7 450 /435 benchmarks and performance
With these being the platforms that you’ll find in most devices this year, I’ll quickly touch on their capabilities and performance expectations.
However, I haven’t tested any of these 2026 devices yet, so I will update this section once we get to test the 2026 Ryzen AI 400 platforms.
In the meantime, I’ll leave you with some numbers for the Ryzen AI 300 counterparts tested in the past (and we already explained that the Ryzen AI 400 platforms are going to perform more or less similarly).
— updating
| AMD Ryzen AI 9 HX 370 + Rad 890M, ~80W – ProArt P16 |
AMD Ryzen AI 9 365 + Rad 880M, ~50W – Yoga Pro 7 |
AMD Ryzen AI 9 HX 370 + Rad 890M, ~33W mode – Zenbook S16 |
AMD Ryzen AI 9 365 + Rad 880M, ~25W mode – Yoga Pro 7 |
AMD Ryzen AI 7 350 + Rad 860M, ~28W mode – Zenbook 14 |
|
| 3DMark – Fire Strike | 8706 (G – 9591, P – 26877, C – 3280) | 8835 (G – 9563, P – 28655, C – 3388) | 7505 (G – 7946, P – 25618, C – 3031) | 7925 (G – 8626, P – 23070, C – 3055) | 6701 (G – 7388, P – 23946, C – 2413) |
| 3DMark – Time Spy | 3836 (Graphics – 3462, CPU – 9903) | 3853 (Graphics – 3462, CPU – 10712) | 3598 (Graphics – 3241, CPU – 9599) | 3503 (Graphics – 3164, CPU – 8944) | 2893 (Graphics – 2577, CPU – 9511) |
| Uniengine Superposition – 1080p Extreme | 1911 | 1809 | 1600 | 1628 | 1304 |
| CineBench R23 (best run) | 19074 cb – multi core, 2002 cb – single core |
19286 cb – multi core, 1966 cb – single core |
17484 cb – multi core, 1950 cb – single core |
13626 cb – multi core, 1956 cb – single core |
14436 cb – multi core, 1948 cb – single core |
| Blender 3.01 – Classroom scene – CPU Compute |
4m 29s | 5m 28s | 5m 12s | 6m 41s | 7m 15s |
| SPECviewperf 2020 – 3DSMax: | 45.34 | 44.52 | 40.95 | 39.75 | 36.94 |
| SPECviewperf 2020 – Catia: | 39.43 | 40.00 | 33.25 | 36.66 | 35.63 |
| SPECviewperf 2020 – Maya: | 150.32 | 141.58 | 125.32 | 134.45 | 93.85 |
These results showcase a few interesting things:
- the Ryzen 9 x70 and x65 processors are close in CPU performance in mid-power implementations, with some advantages for the x70 CPU in longer sustained loads.
- the Radeon 890M in the x70 holds a 15-20% advantage in GPU performance over the Radeon 880m in the x65;
- the Ryzen AI 7 is still a competitive CPU with its 4x Zen5 4xZen5c design, close to the other two in low to mid-powered notebooks;
- the Radeon 860M in the Ryzen AI 7 still scores at about 60-65% of the Radeon 890M, despite having half the CUs;
- expect the Ryzen AI 9 470, Ryzen AI 9 465 and Ryzen AI 7 450 to perform within a few percent of their Ryzen 300 counterparts;
- the Ryzen AI 7 445 with its 2x Zen5 4x Zen5c design will run about 10-15% slower than the AI 7 450 (and AI 7 350) in sustained CPU loads, but otherwise match its capabilities.
List of Laptops built on AMD Gorgon Point (Ryzen AI 400) hardware
This section lists all the available notebooks built on Gorgon Point hardware, with either the upper-level Ryzen AI 9 specs implementation in more powerful devices (sometimes alongside Nvidia dedicated graphics), or the mid-level Ryzen AI 7 450/ Ryzen AI 7 445 meant for ultraportable designs and more affordable options.
The specs for each series can get a little confusing now that these platforms have been unified, so it’s important to understand the particularities of each AMD processor.
This list is a work in progress, and we’re upgrading the article as new units are announced. If you spot any device that should be in here and is not yet, let us know about it in the comments section at the end of the article.
Note: I’ve only included laptops here for now, so none of the mini-PCs and handhelds formats. Might change that in the near future.
| Model | Format, Weight | Screen | Hardware and particularities | Battery |
| Acer Aspire 14 AI | entry-tier ultrabook, 1.27 kg / 2.8 lbs |
14″ 16:10, OLED or IPS up to 3K 120Hz, touch or non-touch 180-hinge |
up to AMD Ryzen AI 7 445, max 32 GB LPDDR5x RAM, 1x M.2 SSD |
65 Wh |
| Acer Aspire 16 AI | entry-tier ultrabook, 1.55 kg / 3.4 lbs |
14″ 16:10, OLED or IPS up to 3K 120Hz, touch or non-touch 180-hinge |
up to AMD Ryzen AI 9 465, max 32 GB LPDDR5x RAM, 1x M.2 SSD |
65 Wh |
| Acer Swift Go 16 AI | mid-tier portable laptop, all-metal build, 1.6 kg / 3.5 lbs |
16″ 16:10, OLED 2K 60Hz touch on non-touch, 180-hinge |
up to AMD Ryzen AI 9 465, max 32 GB LPDDR5x RAM, 2x M.2 SSD, ~45W TDP; dual-fan single-heatsink dual-heatpipe cooling |
65 Wh |
| Acer Nitro V 16 AI | mid-tier all-around laptop, mostly metal build, 2.1 kg / 4.65 lbs |
16″ IPS, matte, 2K 180Hz |
up to AMD Ryzen AI 9 465, RTX 5070 ??W max 32 GB DDR5 RAM, 2x slots, 2x M.2 SSD, dual-fan quad-exhaust cooling |
76 Wh |
| Asus ROG Zephyrus G14 | premium portable laptop, premium metal build, 1.5 kg / 3.31 lbs |
14″ 16:10 OLED 3K 120Hz, glossy non-touch |
up to AMD Ryzen AI 9 465, RTX 5060 90W, max 32 GB LPDDR5x, 1x M.2 SSD ~120W TDP; advanced cooling |
73 Wh |
| Asus TUF Gaming A14 | mid-tier portable laptop, part metal build, 1.46 kg / 3.22 lbs |
14″ 16:10 IPS 2.5K 165Hz, matte non-touch |
up to AMD Ryzen AI 9 465, RTX 5060 105W, max 32 GB LPDDR5x, 2x M.2 SSD ~130W TDP; advanced cooling |
73 Wh |
| Asus ExpertBook B3 G2 14 | mid-tier laptop, part metal build, 1.4 kg / 3.1 lbs |
14″ 16:10 IPS, up to 2.5K 144Hz; matte non-touch |
up to AMD Ryzen AI 9 HX 470, max 96 GB LDDR5, 2xDIMMs, 2x M.2 SSDs |
42,70 Wh |
| Asus ExpertBook B3 G2 16 | mid-tier laptop, part metal build, 1.8 kg / 3.9 lbs |
16″ 16:10 IPS, up to 2.5K 144Hz; matte non-touch |
up to AMD Ryzen AI 9 HX 470, max 96 GB LDDR5, 2xDIMMs, 2x M.2 SSDs |
42,70 Wh |
| Asus ExpertBook P5 G2 14 | business portable laptop, metal build, 1.3 kg / 2.85 lbs |
14″ 16:10 IPS or OLED, matte, glossy non-touch |
up to AMD Ryzen AI 9 HX 470, max 96 GB LDDR5, 2xDIMMs, 2x M.2 SSDs ~45W TDP; |
70 Wh |
| Asus ExpertBook P5 G2 16 | business portable laptop, metal build, 1.6 kg / 3.55 lbs |
16″ 16:10 IPS or OLED, matte, glossy non-touch |
up to AMD Ryzen AI 9 HX 470, max 96 GB LDDR5, 2xDIMMs, 2x M.2 SSDs ~45W TDP; |
70 Wh |
| Asus Vivobook S14 M3407 | mid-tier ultrabook, metal build, 1.4 kg / 3.1 lbs |
14″ 16:10 OLED 2K 60Hz, non-touch |
up to AMD Ryzen AI 7 445, max 32 GB LDDR5, 1xDIMM, 1x M.2 SSD ~35W TDP; |
70 Wh |
| Asus Vivobook S16 M3607 | mid-tier ultrabook, metal build, 1.7 kg / 3.75 lbs |
16″ 16:10 IPS touch or OLED non-touch 2K 120Hz |
up to AMD Ryzen AI 9 465, max 32 GB LDDR5, 1xDIMM, 1x M.2 SSD ~35W TDP; |
70 Wh |
| Asus Zenbook 14 | mid-tier ultrabook, all-metal build; 1.2 kg / 2.65 lbs |
14″ 16:10 OLED up to 2K 120Hz, mostly non-touch |
up to AMD Ryzen AI 7 445, max 32 GB LPDDR5x RAM, 1x M.2 SSD, ~28W TDP; single-fan single-heatsink single-heatpipe cooling |
75 Wh |
| Asus Zenbook S16 | premium ultrabook, all-metal build; 1.5 kg / 3.3 lbs |
16″ 16:10 OLED 3K 120Hz, mostly touch |
up to AMD Ryzen AI 9 HX 470, max 32 GB LPDDR5x RAM, 1x M.2 SSD, ~35W TDP; updated vapor-chamber cooling |
83 Wh |
| HP EliteBook X G2a 14 | business laptop, premium, clamshell, from 1.12 kg / 2.47 lbs |
14″ 16:10 IPS/OLED up to 3K 120Hz, matte or touch. 150-degree hinge |
up to AMD Ryzen AI 9 HX PRO 470, max 64GB LPDDR5x RAM, 1x M.2 SSD |
56 Wh |
| Lenovo Legion 5a | mid-range all-rounder, 1.9 kg / 4.15 lbs |
15.3″ 16:10 OLED 2.5K 165Hz, non-touch |
up to AMD Ryzen AI 9 465, RTX 5060 115W, max 64 GB DDR5, 2x DIMMs, 2x M.2 SSD ~140W TDP; advanced cooling |
80 Wh |
| Lenovo Legion 7a | premium all-rounder, all metal build, 1.85 kg / 4.05 lbs |
16″ 16:10 OLED 2.5K 240Hz, non-touch |
up to AMD Ryzen AI 9 HX 470, RTX 5060 115W, max 64 GB LPDDR5x, 2x M.2 SSD ~140W TDP; advanced cooling |
84 Wh |
| LG Gram 16 | premium ultrabook, 1.2 kg / 2.65 lbs |
16″ 16:10 IPS 2.5K 60Hz, matte |
up to AMD Ryzen AI 7 450, max 32 GB LPDDR5x RAM, 1x M.2 SSD |
77 Wh |
| LG Gram Pro 14 | premium ultrabook, 1.12 kg / 2.5 lbs |
14″ 16:10 IPS 2K 60Hz, matte |
up to AMD Ryzen AI 5 435, max 32 GB LPDDR5x RAM, 1x M.2 SSD |
72 Wh |
| Lenovo Yoga 7a 2-in-1 14 | mid-range 2-in-1 ultrabook, 1.4 kg / 3.1 lbs |
14″ 16:10 OLED 2.8K 120Hz, touch |
up to AMD Ryzen AI 7 445, max 32 GB LPDDR5x RAM, 1x M.2 SSD single-fan with dual-heatpipe |
70 Wh |
| Lenovo Yoga 7a 2-in-1 16 | mid-range 2-in-1 ultrabook, 1.8 kg / 4 lbs |
16″ 16:10 OLED 2.8K 120Hz, touch |
up to AMD Ryzen AI 7 445, max 32 GB LPDDR5x RAM, 1x M.2 SSD single-fan with dual-heatpipe |
70 Wh |
| Lenovo Yoga Slim 7a | mid-range portable ultrabook, 1.15 kg / 2.55 lbs |
14″ 16:10 OLED 2.8K 120Hz, touch or non-touch |
up to AMD Ryzen AI 7 445, max 32 GB LPDDR5x RAM, 1x M.2 SSD dual-fan with single heatpipe |
70 Wh |
That’s about it for this article.
But as mentioned already, stay around, we’re constantly updating these lists of laptops built on AMD’s Gorgon Point Ryzen AI 400 Series hardware, adding new launches as they are released.











NikoB
January 16, 2026 at 5:30 pm
The most boring year (and with minimal demand) in IT technology for ordinary consumers has begun. Nothing new. Nothing truly faster than the 2024 models (the Max+ AI 395, which AMD itself conceived as flawed from the start). It's supposedly the year of "AI," but the market lacks equipment for home (pre-)training or even for truly acceptable inference speed for LLM with at least 500 billion parameters. There's no RAM, no RAM controllers, no IGPU/NPU capable of running such models on home (private) equipment for acceptable money. This is the year of ordinary citizens rethinking what a "consumer" now means to corporations, which have openly declared that they don't care about social responsibility or progress. Their key beneficiaries care only about profit and nothing more…
Also note the complete dominance of OLED models in 2026 (the first year things got worse was 2025), with screens that are extremely dangerous for your eyes (and nervous system) today. Flickering, glare, burn-in, and, crucially, a poor-quality, vision-damaging subpixel structure (which, after a wave of criticism, was hastily corrected in new models with RGB Stripe in OLED, but so far only in rare monitor panels; it's just as bad in laptops): https://nuxx.net/blog/2026/01/09/oled-not-for-me/
IPS options simply no longer exist. We're being forced to buy obviously inferior and dangerous screens without any alternative, just as they were previously forced on smartphones (if you want top-end photo/video cameras and everything else, you'll have to buy (AM)OLED).
Instead of high-quality 4K IPS 1500:1+ for long-term text and graphics work without eye strain in laptops and 8K IPS in monitors (a bunch of worthless 6K models instead).
Once again, interests are skewed toward a tiny group of gamers—not working people—who spend hours staring at static screens at home and at work, because the gaming crowd is willing to pay more and the margins are much higher.
Meanwhile, all SoC capabilities are intentionally (for marketing reasons) blocked from being exposed (including advanced ports, which the buyer actually paid for as part of the SoC) in the entry-level and mid-range lines, and not everything looks acceptable in the higher-end models.
The world has gone in the wrong direction, not toward a place where common sense, critical thinking, and rationality in everything, as well as the desire for progress rather than regression for everyone, reign supreme.
Andrea, I wish you success in critically understanding what is happening in the laptop market and in the industry as a whole.
"Happy" New Year, everyone.
Andrei Girbea
January 16, 2026 at 10:18 pm
I personally prefer good IPS matte displays myself, which are very rare on portable laptops these days.
The subpixel strutcture that the article mentions, however, is less of an issue on a 14-16 inch panel than on a large 34-inch monitor. Flickering and glare, yep, those are there and bother me as well.
NikoB
January 17, 2026 at 6:19 pm
Hello Andrei (sorry I misspelled your name).
Regarding the fact that it's less noticeable on 14-18" (AM)OLED screens, the point is, as I've written many times before, that all modern browsers
(except Firefox, where you can disable anti-aliasing altogether, which I've been using for many years and it's my main browser for reading text, and is generally the best on the market, although it has a number of drawbacks – like the lack of automatic translation from other languages like Chrome and less compatibility with Chrome-specific websites, which has an overwhelming market share due to its quality. And on YouTube, Chrome obviously works much better with hardware acceleration, although without it, Firefox immediately wins on very old hardware without hardware VP9/AV1 decoders – and AV1 is the only decoder available in 8K resolution on YouTube, according to Google, although VP9 was previously available)
have a priori, non-disableable, incorrect anti-aliasing, both in grayscale and in color, in the form of ClearType (and also worse, given the aforementioned defects of the typical subpixel structure of (AM)OLED on laptops and most monitors). Anyone can easily verify this (most people are accustomed to blurry text on laptops and monitors with ppi below 150, which is most often, which is surprising and astonishing, since everyone has a smartphone with ppi 300+, where the text looks like it was printed on a laser printer) simply by taking a screenshot of the page in Chrome/Edge/Firefox (with default settings) and enlarging it in Paint by 400-500% to see for yourself the vertical shadows around all the characters, which should not be there with proper grayscale anti-aliasing – they never are there. The last browser that had proper grayscale anti-aliasing, as it was in XP, was Firefox v68 (with certain settings). Then things got really bad. All browser developers are well aware of this defect (there are old entries from professionals on the Chrome bug tracker), but they did nothing They're fixing it.
This defect only becomes unnoticeable at ppi levels above about 220-230. 300+ is better. And that's why it's never visible on smartphone screens; the pixels are too small. On laptop screens, this defect can only become unnoticeable with 3.2k (as well as 2.5k/2.8k) panels, but 3.2k isn't pixel-compatible with 8k/4k/FHD content, meaning it doesn't divide FHD evenly. 4k/8k isn't evenly divisible.
Obviously, the only correct option is true RGB 4k panels, but they're rarely installed even in expensive laptop models, and never in mainstream models (although the price difference with 2.5k/DCI-P3 is minimal in reality).
Although they (4k) should have become the most common laptop screens on the planet 6-7 years ago.
But unfortunately, they haven't reached the same level as smartphone screens with 300+ ppi. In monitors, only 6K panels provide the minimum 220-230 ppi, but again, 6K doesn't even perfectly divide 8K, nor does it even divided by 4K or FHD, so we again end up with a blurry picture at the pixel level, unlike 8K panels, which are universal and should have been standard in all monitors by now. They're ideal for everyday work with text and graphics and for gaming, because 8K is perfectly divisible by 4K and FHD, meaning there's no problem switching the monitor to 4K or FHD when needed (many gamers play on 27" FHD monitors) and getting perfect pixel sharpness in games at 240Hz+.
Thus, to eliminate all the problems described above for the human eye, only two resolutions should have remained on the market long ago: 8K for monitors and 4K for laptops.
Unfortunately, 8K over a single cable without lossy compression can only be achieved through a DP2.0+ port in UHBR20 mode (80Gbps) or via TB5 tunnel (up to 120Gbps). It can also be achieved through the future (and already obsolete) HDMI 2.2 with 96Gbps, which is still missing from hardware. Meanwhile, hardware manufacturers delayed implementing DP2.0/UHBR20 for five years (it was released as a standard in 2019), as did TB5 (which is a proprietary technology, although DP ports now also require licensing fees).
As a result, mass 8K monitors became possible only from 2025 (mass gpus get UHBR20 mode support), but for some reason there are practically none on the market yet, but as I see (analyzing the market), the capitalists clearly decided to first collect money on 6K resolution (which is bad for the above-mentioned reasons of incompatibility at the pixel level with FHD/4K/8K content) before rolling out to the public the final 8K for human eyes – after it, replacing a 27-34" monitor will become practically meaningless until the complete physical failure of the monitor (and this is 10-15 years if the panel resource is at least 50K hours up to 50% loss of brightness). Despite the fact that 8K monitors were shown back in 2013, i.e. 12 years ago (a whole era!), we still won’t see mass 8K monitors in 2026 and 2027, apparently either. The capitalists will first cultivate the masses on 6K resolution. Moreover, their the primary target audience of interest is the high-margin target audience—gamers, not work class.
As I mentioned earlier, high-frequency PWM is only promised for (AM)OLEDs in smartphones by 2025. Such advances in laptop and monitor panels, if they are truly feasible, have yet to be realized. Furthermore, glossy finishes, as we see in laptop models, are also ubiquitous, with no consumer choice (semi-matte screens are offered on very few monitor models). Subpixel structure defects in laptop panels are also unavoidable; there are currently no (AM|)OLED panels with an RGB stripe structure like IPS/VA. And of course, burn-in issues have not been realistically addressed in the real-life lifespans of laptops and monitors—at least 6-7 years for the former and 10-15 years for the latter. Especially now, when performance per watt of consumption is slowing rapidly – even smartphones are replaced no more than every 4-5 years (global statistics), while laptops are a longer-lasting product, much less monitors (high-quality ones). There's no point in replacing a good, high-quality monitor for more than 10 years, unless it burns out.
Even more, there's no practical point in replacing a monitor with an 8K panel, provided the refresh rate is 120Hz or higher and the response time matches it. 120Hz is currently achievable without lossy compression only in 24-bit color (which is insufficient even for 4K resolution to eliminate dynamic banding) and only over TB5 in 120Gbps mode. 30/36-bit color requires a bandwidth of 160Gbps. And this, as I've written many times before, is most likely a forced transition to fiber optics (it's long past time to abandon copper cables), which will also allow cables much longer than 2 meters, offering new options for the mass consumer in the fight against noise (moving noisy equipment to another room or utility room).
I've attempted to comprehensively describe the current technological situation and why manufacturers are so clearly opposed to the introduction of 4K panels in laptops and 8K monitors. Although, looking at the way retail prices for those same laptops fluctuate across retail chains, it's downright laughable when some object to the increased price. The price difference between the same model in two neighboring retail chains, even in the US, can reach 1-2 times the retail price of a 4K panel ($150-160 for an A++ grade) for a medium class laptop. I've personally observed this many times in markets around the world. Therefore, I immediately dismiss price arguments in laptops. Even from the perspective of entry-level office models like $500-600, the difference in image quality in browsers is so great that if a person were to choose between a $600 laptop with a 16” FHD IPS and a 16” 4K IPS laptop for $750, you can bet that any buyer would choose the second option without hesitation, paying the extra cost. And in more expensive models there will be no dispute, but nevertheless, laptop manufacturers are still putting miserable 2.5k even on 18”, and only a couple of models have 4k (MSI Titan / Lenovo L9 18” – but here Lenovo screwed up again – putting only glossy panels), which can’t be called mass-market, especially if a person just needs an 18” home laptop with 4k IPS 1500:1+ and without a discrete graphics card – ideally with Max+ AI 395, which again, a whole year later, is almost completely absent from business models, but it is widely available in Chinese miniPCs. Which is a very strange policy for AMD and laptop manufacturers. The best universal SoC was absent from 16”-18” laptops even in the spring and summer of 2025, RAM cost literally pennies, and the Chinese sold MiniPCs with 128GB LPDDR5X 8000/2T SSD en masse from $1,500…
That's why I wrote earlier – the world has clearly gone in the wrong direction in terms of mass technology (and in general), and this trend will be fully entrenched in 2025.
Andrei Girbea
January 20, 2026 at 10:07 am
Thanks, Niko. I appreciate the time for explaining this! I haven't personally looked so closely into it. For what is worth, I use an 18-inch IPS 2.5K laptop as a daily driver, paired to a high-quality IPS 4K display, and of course, everything looks sharper and nicer on the monitor (but that is a very expensive monitor). Not a fan of OLEDs due to glare, without even considering the other reasons, but matte OLEDs with Gorilla Glass matte are starting to be a thing this year.
I'll just add that 18" laptops are still a niche, but I would like to see the Halo hardware implemented in more mainstream 16-inch options. However, from the looks of it, there are still very few laptop-formats announced with Halo this year. Pretty much just two new ones from Asus, the ProArt PX13 and the TUF A14. Nothing else. So I'd reckon we won't see many more devices this year, but only next year with Medusa Halo or whatever the next-gen AMD hardware ends up being called.
Good point on Halo hardware implemented in all sorts of miniPCs and handhelds as well, but not in laptops. I too wonder what's the reason for it.
NikoB
January 22, 2026 at 7:20 pm
Hi Andrei,
18" 2.5k (16:10) ~ 167 ppi
27"+ 4к (16:9) ~ <=163 ppi.
Anything larger diagonally in 4K has a lower ppi, which requires 8K. In terms of pixel sharpness, this is a problem with the subpixel structure. This isn't a problem with regular Stripe RGB IPS panels; it's a problem with (AM)OLEDs, excluding the new Stripe RGB panel variants (and even there, the subpixel structure doesn't exactly replicate the IPS structure).
What's the point of a high ppi on a monitor/laptop panel? With a pixel invisible to the eye, at any distance from the screen (100% analog image), the spontaneous refocusing of the eye from objects on the screen to the pixel structure is eliminated. You can see that the object isn't actually monolithic, but is broken up into pixels, i.e., A discrete structure, which is bad (imagine if you could see objects in the real world and see their discrete structure; how terrible that would be, although in reality, at the atomic level, all matter is discrete). If we consider the minimum distance to be 20-25 cm from the screen, then the limit is reached. That is, no matter how far a person's head moves from the screen, they always 100% see a perfect analog image, not the pixel structure of the matrix. This is the whole point – to remove the stress from spontaneous refocusing on the visible pixel structure. The better a person's vision, the worse it gets on low-ppi screens – spontaneous refocusing will be more frequent.
On smartphones, people (especially those with mild myopia, who usually see much better up close than people with normal vision, and especially those with farsightedness (people with this problem generally cannot see anything up close, and farsightedness develops more often with age) can easily discern pixels from 20-25 cm away, even at 300 ppi. At approximately 380-400 is simply not realistic for anyone at any distance. But with monitors, the typical viewing distance is 40cm+ (at which 140-180 ppi pixel structure is still clearly visible), even with laptops.
To get a significantly better picture on a 27"+ than on an 18" 2.5k panel, you need a 6k panel (and so on up to about 31.5"), but 6k isn't universal in terms of compatibility with 8k/4k/FHD video content. That's the problem. Whatever you do, we're returning to the strict requirement for 8k on monitor diagonals and 4k on laptops. Unfortunately, we'll have to wait a very long time, as 6k monitors have begun to be launched en masse (they're coming out one after another, to my disappointment), not 8k, although ports in mainstream hardware will definitely be ready for 8k by 2026, as will hardware in general. 2D/light 3D. 8K panels in monitors would immediately solve the whole issue of screens in terms of pixel structure visibility.
I'll probably be an older pensioner with poor eyesight by the time 8K monitors become widespread. Given my active lifestyle, that's already becoming unrealistic.
NikoB
January 22, 2026 at 7:50 pm
Regarding the 395th (and the general state of the hardware market) – I am increasingly shocked that more and more new MiniPCs with this SoC are being announced on the market in 2026 (and most of them are poorly made and have cut off ports from the SoC), but no 16-18" laptops from famous brands. They are clearly not commercially interested in promoting such models. But for some reason, it is interesting to the Chinese with MiniPCs, which, of course, are bought by orders of magnitude fewer buyers than laptops and gaming laptops. Apparently, most buyers are interested in gaming solutions with a price tag above about $ 1,500 (and this bar itself is gradually shifting upward along with the rapid devaluation of the dollar and other reserve currencies). But this again speaks of the reduction of the productive layer of people on the planet to very small groups of the population (from the point of view of intellectual product development), which are no longer of interest to large laptop manufacturers to create such narrow lines for them (like the Legion 9 18" with a semi-matte screen, but Without a dGPU, but with Max+ AI 395 and without the teenage illumination). Apparently, this is the key reason. The worst thing is to end up in a marginal group of potential buyers (in terms of profitability for large multinational corporations).
Previously, the masses sponsored the production of increasingly sophisticated motherboards and PCs, then laptops. But around 2012, interest in the PC market began to fade very rapidly, and in the laptop market around 2017 (a critical phase in the spread of smartphones worldwide). This is because the general population has switched to smartphones. They don't need anything else in everyday life. And in poor countries, smartphones are often the only computers in the home, performing everything the average consumer needs (and they simply don't have the money for more) and are always with them. Meanwhile, laptops and PCs are becoming increasingly specialized tools with gradually decreasing demand. Roughly, smartphone users can be divided into consumers, while laptop and PC users are more likely to be content creators (excluding the gaming crowd) or those with requirements that go beyond the typical consumer. For this reason, the quality of laptops and PCs has rapidly declined—there's no longer a mass "sponsor" for improving laptops and PCs. And recently, this mass "sponsor" has begun to falter in the smartphone market as well (which was also expected)—the frequency of model upgrades has rapidly declined.
And the professional segment, with its strict requirements, is rapidly growing in price (because professionals clearly understand what they need and what they can't compromise on, unlike the technically illiterate average consumer, who readily accepts cheap 45-46% NTSC screens in mass-market laptops, for example). Despite population growth, such solutions are increasingly rare (rare in demand).
And given the increasing fears of automation/robotics and the replacement of white-collar workers by AI (most of these claims are, of course, pure marketing and market hype, designed to drive down the wages of the average "middle class" worker or force them to work much harder for the same nominal fiat currency), it's clear that mass-market products will become increasingly less useful for professional use. The solvent "middle class" is disappearing. The world is increasingly dividing between rich and poor. And the space between them is becoming increasingly empty… The rich are shedding crocodile tears at "Davos" conferences, realizing that the marginalization of ever-increasing numbers of "middle class" people thanks to their efforts presents them with an increasingly existential problem of personal survival, should these marginalized people suddenly unite.
The goal of modern TNCs and businesses is to tie everyone to a paid, permanent subscription (they've long since removed perpetual licenses, much like real estate players are buying up family homes en masse to get everyone hooked on renting rather than owning, manipulating prices) and turning your device into a mere cloud terminal (of which you're not actually the owner; this has long been the case with smartphones—most don't have root access to the supposedly purchased product, and now even bootloader unlocking or root access is increasingly rare. Imagine the same thing on laptops or PCs—you're not the administrator of your own device. M$ is diligently leading us to exactly this. PC/laptop buyers have traditionally been more technically literate and generally had a better education, outlook, and mentality than mass smartphone buyers, where such an inherently totalitarian policy (disguised as "security") easily permeates the illiterate masses). Without local storage (if possible). So that the average consumer is maximally dependent on this infrastructure. And the TNCs are giving power that was previously unimaginable. I'm apparently on the opposite side of the spectrum, and it's hard for me to watch all this, given the life I've already traveled.
Andrey, publishing this comment is at your own discretion.